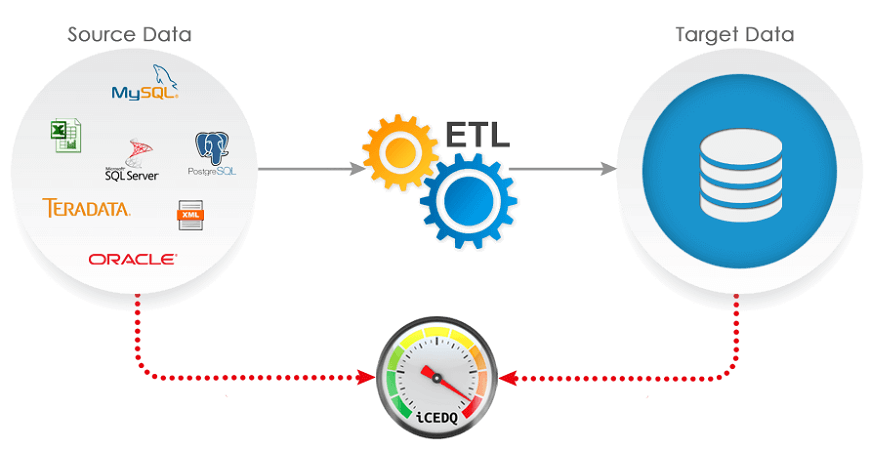
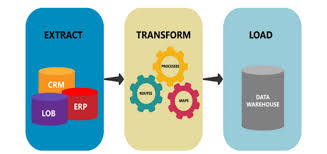
ETL comes from Data Warehousing and stands for Extract-Transform-Load. ETL covers a process of how the data are loaded from the source system to the data warehouse. Currently, the ETL encompasses a cleaning step as a separate step. The sequence is then Extract-Clean-Transform-Load. Let us briefly describe each step of the ETL process.
Process
Extract
The Extract step covers the data extraction from the source system and makes it accessible for further processing. The main objective of the extract step is to retrieve all the required data from the source system with as little resources as possible. The extract step should be designed in a way that it does not negatively affect the source system in terms or performance, response time or any kind of locking.
There are several ways to perform the extract:
- Update notification – if the source system is able to provide a notification that a record has been changed and describe the change, this is the easiest way to get the data.
- Incremental extract – some systems may not be able to provide notification that an update has occurred, but they are able to identify which records have been modified and provide an extract of such records. During further ETL steps, the system needs to identify changes and propagate it down. Note, that by using daily extract, we may not be able to handle deleted records properly.
- Full extract – some systems are not able to identify which data has been changed at all, so a full extract is the only way one can get the data out of the system. The full extract requires keeping a copy of the last extract in the same format in order to be able to identify changes. Full extract handles deletions as well. Learn more from ETL Testing Training
When using Incremental or Full extracts, the extract frequency is extremely important. Particularly for full extracts; the data volumes can be in tens of gigabytes.
Clean
The cleaning step is one of the most important as it ensures the quality of the data in the data warehouse. Cleaning should perform basic data unification rules, such as:
- Making identifiers unique (sex categories Male/Female/Unknown, M/F/null, Man/Woman/Not Available are translated to standard Male/Female/Unknown)
- Convert null values into standardized Not Available/Not Provided value
- Convert phone numbers, ZIP codes to a standardized form
- Validate address fields, convert them into proper naming, e.g. Street/St/St./Str./Str
- Validate address fields against each other (State/Country, City/State, City/ZIP code, City/Street).
Transform
The transform step applies a set of rules to transform the data from the source to the target. This includes converting any measured data to the same dimension (i.e. conformed dimension) using the same units so that they can later be joined. The transformation step also requires joining data from several sources, generating aggregates, generating surrogate keys, sorting, deriving new calculated values, and applying advanced validation rules. Get more from ETL Testing Course
Load
During the load step, it is necessary to ensure that the load is performed correctly and with as little resources as possible. The target of the Load process is often a database. In order to make the load process efficient, it is helpful to disable any constraints and indexes before the load and enable them back only after the load completes. The referential integrity needs to be maintained by ETL tool to ensure consistency.
Managing ETL Process
The ETL process seems quite straight forward. As with every application, there is a possibility that the ETL process fails. This can be caused by missing extracts from one of the systems, missing values in one of the reference tables, or simply a connection or power outage. Therefore, it is necessary to design the ETL process keeping fail-recovery in mind.
Staging
It should be possible to restart, at least, some of the phases independently from the others. For example, if the transformation step fails, it should not be necessary to restart the Extract step. We can ensure this by implementing proper staging. Staging means that the data is simply dumped to the location (called the Staging Area) so that it can then be read by the next processing phase. The staging area is also used during ETL process to store intermediate results of processing. This is ok for the ETL process which uses for this purpose. However, tThe staging area should is be accessed by the load ETL process only. It should never be available to anyone else; particularly not to end users as it is not intended for data presentation to the end-user.may contain incomplete or in-the-middle-of-the-processing data.
ETL Tool Implementation
When you are about to use an ETL tool, there is a fundamental decision to be made: will the company build its own data transformation tool or will it use an existing tool?
Building your own data transformation tool (usually a set of shell scripts) is the preferred approach for a small number of data sources which reside in storage of the same type. The reason for that is the effort to implement the necessary transformation is little due to similar data structure and common system architecture. Also, this approach saves licensing cost and there is no need to train the staff in a new tool. This approach, however, is dangerous from the TOC point of view. If the transformations become more sophisticated during the time or there is a need to integrate other systems, the complexity of such an ETL system grows but the manageability drops significantly. Similarly, the implementation of your own tool often resembles re-inventing the wheel.
There are many ready-to-use ETL tools on the market. The main benefit of using off-the-shelf ETL tools is the fact that they are optimized for the ETL process by providing connectors to common data sources like databases, flat files, mainframe systems, xml, etc. They provide a means to implement data transformations easily and consistently across various data sources. This includes filtering, reformatting, sorting, joining, merging, aggregation and other operations ready to use. The tools also support transformation scheduling, version control, monitoring and unified metadata management. Some of the ETL tools are even integrated with BI tools.
To get in-depth knowledge, enroll for a live free demo on ETL Testing Certification