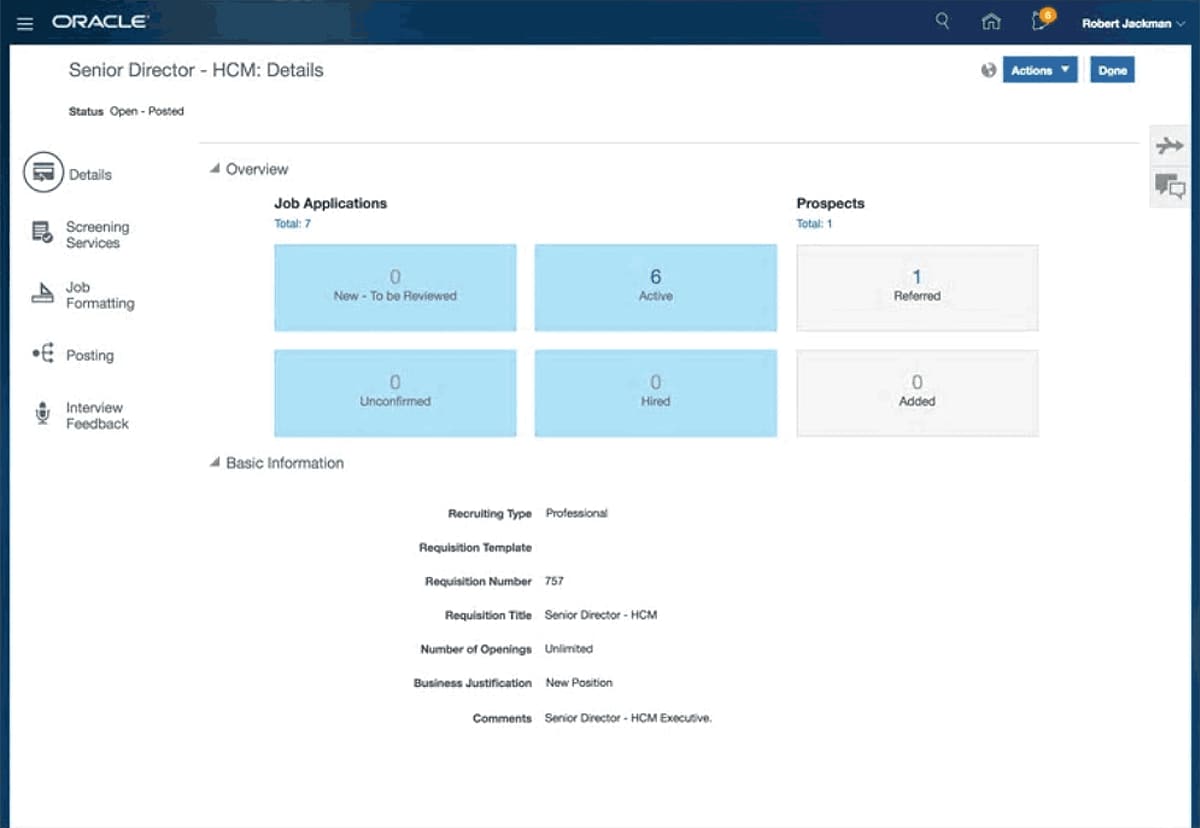
The ServiceNow® Event Management application helps you to identify health issues across the datacenter on a single management console. It provides alert aggregation and root cause analysis (RCA) for discovered services, application services, and automated alert groups. Event Management is available as a separate subscription from the rest of the Now Platform.
Understanding Event Management
Monitor the health of services and infrastructure using a single management console and respond appropriately to any issues that come up. Event Management provides intelligent event and alert analysis to ensure continuity of your services’ performance. Event Management receives and processes events via the MID Server.
What Event Management can manage
Event Management can manage:Discovered servicesA service is a definition of interrelated CIs from the CMDB. The discovered service, from Service Mapping, includes a service map with: mapping relationships, an impact tree showing outage severity, active alerts, related alerts, and CI properties. Service information is discovered by Service Mapping. The mapping information appears on dashboards, the Alerts list, and the Events list.Application servicesAn application service is a service created by selecting CIs to include in the service. Application service information appears on dashboards with drill-down capability to a map view.Technical servicesA Technical service is a dynamic grouping of CIs, based on some common criteria. For example, you can create a technical service based on location for all web servers or all databases in Ireland.Alert groupsAlert groups show sets of alerts for ease of maintenance.
Architecture
As events occur on various systems, the MID Server connector instance sends the events to the instance. Event Management generates alerts, applies alert management rules, and prioritizes alerts for remediation and root cause analysis. View this information on dashboards, the alert list in Alert Intelligence, or from a service map.

Workflow
Event Management receives external events and generates alerts based on event and alert management rules. Events are sent directly to your instance using an email server, script, SNMP trap, or a web service API. The corresponding alerts appear on dashboards for tracking and remediation purposes.
As the computer, software, or service generates events, the MID Server polls the external event tracking tool. The MID Server, which maintains a connection to Event Management, sends the information to your instance for storage, processing, and remediation.
The instance stores events in the Event [em_event] table and attempts to generate alerts based on pre-defined rules and event mappings. Regardless of whether an alert generates, the original event is available for review and remediation. Alerts generate according to the following process flow: More info at servicenow Online Training
- Find the best matching event rule for an event. If the source of the event matches the source specified in an existing rule, then a rule is matched. Also, if the event matches the optional rule Filter and the event additional_info value matches the rule Additional Information filter. A rule without any filter is ignored, for example the source filter is missing or the Additional Information filter is missing. If multiple rules are defined for the same type of event, use the rule Order to determine the order of rule application.
- If the rule Ignore check box is selected, no alert generates. However, the event is still available for review and remediation.
- If transforms have been defined, apply them. If compose parameters are set, apply the additional content to display to the user in the alert.
- If Active in the threshold section is selected, accumulate all events until the threshold is met. Generate a single alert for the events.
- Search for an event field mapping even if there was no event rule. If an event field mapping is found, apply the mapping information. If the event has no severity after the event transformations, retain the event for reference purposes and do not generate an alert. Learn more from Servicenow Certification
- Search the Alert [em_alert] table for a matching message key. If a matching message key exists, update the alert according to the event information. If a matching message key does not exist, create an alert. If another event has the same matching key, associate the events under a single alert. For root cause analysis purposes, bind the alert to a specific CI.

Event Management and Service Mapping
Event Management uses discovered services from Service Mapping and automated alert groups with root cause analysis (RCA) to expedite alert resolution.
When an event from an external source arrives from the MID Server, script, or web service API (not pictured), Event Management locates CI information for alert generation and CI remediation. CI information is stored in the CMDB from sources such as Service Mapping, Discovery, third-party sources, and manual population. You can use correlated alert group and root cause analysis information to resolve the issue.

To get in-depth knowledge, enroll for a live free demo on Servicenow Training